Why might a VPN be slow and how can I fix it?
Why Your VPN Might Be Slow and How to Fix It
Today, the internet is a space where every action is tracked and analyzed. Advertising, behavioral tracking, and mass surveillance raise concerns about data security. To protect privacy, tools like Tor and VPNs are used. Tor provides anonymity through onion routing, while VPNs ensure security through data tunneling. This article will help you choose the right tool.
Main Reasons for a Slow VPN
1. Overloaded Servers: When the Queue Doesn’t Move
One of the most common reasons for a slow VPN is server overload. Imagine visiting a popular café during lunch hour with a line stretching out the door. The more people waiting for their order, the longer each person has to wait.
The same happens with VPN servers. When many users connect to a single server simultaneously, its resources are divided among them, reducing the speed of each connection.
Example: You connect to a server in the USA during peak working hours when millions are using VPNs for remote work. The server is overloaded, slowing your connection. Solution? Try selecting a server in a nearby region or wait for a less busy time.
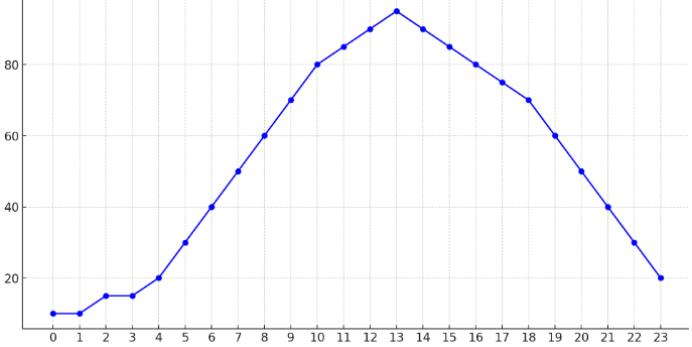
Y=Number of users
X=Time
2. Server Distance: The Farther, the Slower
The physical distance between you and the server matters. The farther the server, the longer it takes for data to travel. It’s like making international calls in the era of landline phones: the more borders crossed, the longer the delay.
Why It Matters
Data passes through multiple intermediate nodes before reaching the server. Each node can slow down the transmission.
Example: You’re in Europe and connect to a server in Australia. Data travels across oceans and continents, slowing the connection. To speed up your VPN, choose a server closer to your current location.
3. Low Bandwidth: The Internet’s Bottleneck
Even the fastest VPN service is limited by your internet connection’s speed. If your provider offers low bandwidth, don’t expect lightning-fast performance.
Factors Affecting Bandwidth:
- An internet plan with limited speed.
- Dozens of devices connected to your network.
- Parallel tasks like downloading large files or streaming in 4K.
Example: You’re working via VPN while your neighbor streams high-quality movies. Your connection speed drops as the bandwidth is shared among all network users. Solution? Disconnect unnecessary devices or ensure you’re using a high-speed internet plan.
Encryption: Protection or a Cause of Slowdowns?
Encryption is the foundation of security in virtual private networks. It’s what protects your data from cyber threats. However, complex encryption algorithms can slow down your internet connection. Why does this happen?
Encryption Protocols: The Speed vs. Security Dilemma
Modern VPN services use various encryption protocols like OpenVPN, IKEv2, and WireGuard. Each has its own characteristics:
- OpenVPN: One of the most secure and reliable protocols, but high encryption levels can demand significant device resources.
- IKEv2/IPSec: A fast and secure protocol, ideal for mobile devices due to its ability to maintain connections during network switches.
- WireGuard: A new encryption standard combining security with high speed due to minimal code.
Example: If your VPN uses OpenVPN with maximum AES-256 encryption, downloading large files may slow down due to increased device load. Switching to a lighter protocol like WireGuard can boost speed.
ISP Throttling: Artificial Speed Limits
Internet service providers sometimes intentionally reduce connection speeds for certain types of traffic. This is called ISP throttling—deliberate bandwidth restriction.
Why Does It Happen?
- Reducing network load. During peak hours, providers may slow certain connections to distribute resources.
- Streaming and torrents. Providers may throttle speeds if they detect heavy video streaming or file downloads via VPN.
- Tariff restrictions. Some plans have speed limits due to provider policies.
Signs of ISP Throttling:
- Slow connections only when using a VPN.
- Sudden speed fluctuations throughout the day.
- High ping and slow loading despite a strong Wi-Fi signal.
Example: A user streaming 4K video via VPN notices constant buffering. After investigation, it turns out the provider is throttling encrypted traffic.
Hardware Limitations: An Unfixable Brake
Even the fastest VPN won’t deliver high speeds if your device or router is outdated or underpowered.
What to Check?
Device Performance:
- Old processors struggle with resource-intensive encryption processes.
- Insufficient RAM can lead to system overload.
Routers and Network Equipment:
- Older router models support outdated Wi-Fi standards (e.g., 802.11n instead of modern 802.11ac or 802.11ax).
- A weak router processor can slow VPN traffic.
Software Updates:
- Outdated network card drivers or old router firmware can reduce network performance.
Example: If a decade-old laptop is connected to a VPN via a router supporting only outdated Wi-Fi standards, even the fastest connection will perform poorly.
How to Fix a Slow VPN: Practical Tips and Effective Solutions
If your VPN connection is slow, there’s no need to sacrifice data protection. Here are several ways to improve speed without compromising security.
1. Choosing the Optimal Server: Closer is Faster
The data path matters. The closer the server, the faster the connection.
Tips for Server Selection:
- Geographic Location: Always choose a server as close as possible to your location.
- Server Load: Check server load indicators. Many VPN clients display this as a percentage or visual indicator.
- Test Connections: Try multiple servers in nearby countries to find the best option.
Example: If you’re in Europe, connecting to a server in Germany will be faster than one in Australia, even if the latter seems more reliable.
2. Checking Your Internet Connection: Start with the Basics
Even the fastest VPN is useless with a slow internet connection.
What to Check:
- ISP Speed: Run a speed test (e.g., via Speedtest) with and without the VPN.
- Device and Network Limits: Reboot your router, disconnect unnecessary devices, and close background apps.
- Wired Connection: Switch from Wi-Fi to Ethernet if possible.
Example: If video streaming lags only when using a VPN but works fine without it, the issue is likely server load or VPN settings.
3. Switching Encryption Protocols: Find the Balance
Sometimes, changing the encryption protocol in your VPN client settings can boost speed without significantly reducing security.
Recommendations:
- For Maximum Speed: WireGuard is the fastest modern protocol.
- For Stability: IKEv2/IPSec is resilient to connection interruptions.
- For Protection: OpenVPN (UDP for speed, TCP for reliability).
Example: If your VPN is slow on OpenVPN, switching to WireGuard often helps with high workloads.
4. Updating Hardware and Software
Outdated equipment can bottleneck network performance.
What to Update:
- Routers: Use modern models supporting Wi-Fi 6 or 5G.
- Computers and Mobile Devices: Update operating systems, drivers, and VPN apps.
- Router Firmware: Ensure your router runs the latest firmware.
Example: Upgrading an old Wi-Fi 4 router to a modern Wi-Fi 6 model can increase data transfer speeds several times.
5. Bypassing ISP Throttling
If your ISP is throttling your VPN, try these solutions:
Ways to Bypass:
- Traffic Obfuscation: Enable obfuscation (if available) to hide VPN usage.
- Port Switching: Use non-standard ports (e.g., 443) to bypass restrictions.
- Switching ISPs: If restrictions are too severe, consider changing your internet provider.
Example: Enabling obfuscation often helps users in countries with strict internet censorship, allowing them to avoid VPN connection blocks.
6. Optimizing VPN Client Settings
Technical settings in your VPN client can significantly impact performance.
Recommended Changes:
- Switch from TCP to UDP: UDP is faster but less reliable, suitable for streaming and gaming.
- Adjust MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit): Reduce MTU if connections frequently drop.
- Split Tunneling: Route only protected traffic through the VPN, leaving other data outside it.
Example: If websites load slowly via VPN, switching to the UDP protocol can significantly speed up the connection.
Conclusion: A Fast VPN — Comfort and Security Online
A slow VPN connection isn’t a dealbreaker—it’s a solvable problem. Proper settings, choosing the right server, updating equipment, and understanding your ISP’s behavior are key to improving speed.
Final Recommendations:
- Connect to the nearest server with minimal load.
- Check your internet connection quality and eliminate network congestion.
- Use modern devices and keep software updated.
- Try switching encryption protocols for a better balance of speed and security.
- Bypass ISP restrictions using obfuscation and non-standard ports.
A fast and reliable VPN is more than just convenience—it’s about protecting privacy, accessing global resources without restrictions, and ensuring data security.
KelVPN: Quantum Security in the Digital World
KelVPN is more than just another VPN service—it’s part of the quantum-secure Cellframe Network ecosystem. The project combines blockchain technology with internet security, creating a decentralized network where every node can act as a full-fledged VPN provider and earn rewards for its services.
Tokenization and Decentralization
At the core of the network is its proprietary blockchain and KEL token, traded on exchanges like UniSwap and PancakeSwap. This makes KelVPN not just a service but part of a decentralized financial ecosystem where users can be both clients and providers.
Platform Availability
KelVPN currently supports four popular platforms:
- macOS
- Android
- Linux
- Windows
This ensures broad compatibility and ease of use across most devices, from home computers to work laptops and smartphones.
Quantum Security: Tomorrow’s Technology Today
The service emphasizes data security, powered by cutting-edge cryptographic protocols:
- CRYSTALS-Dilithium: A quantum-resistant digital signature algorithm capable of withstanding quantum computer threats.
- Kyber 512: A protocol for secure key exchange, ensuring safe connections even under global network attacks.
These technologies are already recommended by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) as future internet security standards. Mass adoption is expected within the next five years, but KelVPN is using them now.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About VPN Speed
1. Why did my VPN suddenly become slow?
Causes range from high server load and distance to ISP throttling. Check your connection, switch servers, or change protocols.
2. Which VPN protocol offers the best speed?
WireGuard provides high speed with solid protection. OpenVPN (UDP) is also fast but may be less stable.
3. Does my internet connection affect VPN speed?
Yes. A VPN uses your existing internet speed, so a slow connection will impact VPN performance.
4. Can I bypass ISP restrictions?
Yes, by using traffic obfuscation, switching ports, or changing providers.
5. Do I need to upgrade hardware for VPN use?
Yes. Modern routers and devices offer better performance and support for new security standards.
6. Can a free VPN slow down my internet?
Yes, free VPNs often limit speed, servers, and traffic, leading to slower connections.
7. What if my VPN speed remains low after all tweaks?
Contact your VPN service’s support or check for app updates. In some cases, switching VPN providers helps.
8. How does server distance affect VPN speed?
The farther the server, the higher the latency and lower the speed. Choose servers closer to your location for optimal performance.
9. Can a VPN speed up my internet connection?
In rare cases, a VPN can bypass ISP throttling, improving speed. However, encryption typically slightly reduces speed.
10. How does the number of users on a server affect VPN speed?
High server load from many users can reduce speed. Try switching to a less crowded server.
11. Why does VPN speed vary at different times of the day?
Server and internet channel loads fluctuate based on user activity. Speeds may drop during peak evening hours.
12. How can I check my real VPN speed?
Use speed tests (e.g., Speedtest) with and without the VPN to compare performance and assess its impact.
With these recommendations, you can optimize your VPN for speed while maintaining a high level of data protection.